P(n)-BST : Partionned Binary Search Tree
A new data structure for distributed environments and parallel treatment
Proposed by D.E ZEGOUR
Previous works and works in progress
Doctorate these 1 Doctorate these 2
Realized by S. ABBAR & CHOUIHA M. A
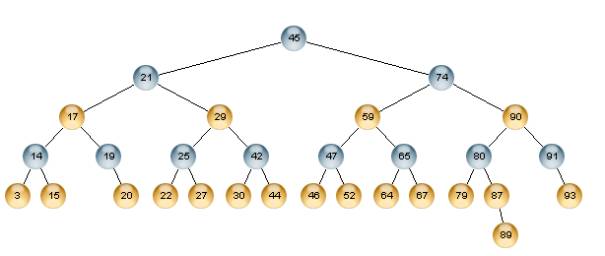
Description :
P(n)_BST is a special balanced binary search tree. It is organized in levels. Each level consists of a set of sub binary search
trees whose the maximal size in nodes is N-1. N being the parameter of the
tree.
In the figure, there are three levels :
level 0 with the subtree 45
level 1 with two subtrees [21, 17, 29] and [74, 59, 90]
level 2 with eight subtrees [14, 3, 15], [19, 20], [25, 22, 27], etc.
This representation allows to partition a set of data according to a given size
n.
A
P(n)-BST node can be of two different types : a simple node and a partition
node. These last nodes define the partition of the tree. Besides
the data field , a simple node contains a field used for the balancing (
balance field). A partition node is a simple node with an additional
field allowing to partition the tree (Partition Field).
The
partition field contains the size of the associated partition. It is
incremented after every insert operation and is decreased after every
delete operation.
This
field manages the tree while we partition the tree. It is invoked in the
specific operations of the P(n) bst : co-balancing,
re partitioning, etc..
By analogy in the Red Black trees and in order to simplify the
presentation of our data structure we can color the tree nodes. For
example, the nodes colored in blue represent the partition nodes
and the ones in yellow the simple nodes
Formally, a PBST(n) can be defined as follows :
(i)
The maximal size of a partition is n-1.
(ii)
Two sister partitions must not have a depth difference superior to
one.
(iii)
The sum of the sizes of two sister partitions is superior to n-1.
(iv ) All the leaf partitions have the same depth
represents simple nodes. A partition contains at most 4 items From bottom to the root and
from left to right, we have the following partitions {3, 14, 15}, { 19, 20}, {22, 25, 27}, {30, 42,
44}, {46, 47, 52}, {64, 65, 67}, {79, 80, 87, 89}, {91, 93}, {17, 21, 29}, {59, 74, 90}, {45}.
When a partition ( a sub tree) reaches n after an insert operation, there
is re structuration (re coloration) of
the tree. In this way, the maximal size of a partition is (n-1) ( One-to-two
partitions transformation)
After a delete operation the sum of two sister partitions can become
smaller than n. A re structuration operation is then undertaken in order
to transform them to only one partition ( Two-to-one partition
transformation)
After an insert or delete operation. the difference in depth between two
sister partitions can become greater than one. A co-balancing
operation is then undertaken. This operation ( re coloration) consists in
modifying the three nodes concerned : the partition nodes of the two
partitions and their father.
Notice that all the branches hold the same number of partition nodes (blue
nodes). This means that the P(n)-BST structure is similar to a B_tree.
Variant 1: PBST_r
The
PBST_r structure is similar to the one of PBST, except that the nodes of
the leaf partitions are duplicated in the non leaf ones. When a leaf
partition splits, the root remains in the left leaf and a copy is
transferred in the father partition. This leads to three types of nodes:Partition
node ( in blue color in the figure), Simple node ( in red color in the
figure), and Index node( in yellow color in the figure).
A simple node exists only in the leaf partition ( the data partition). An index node holds only a data and two pointers to its sons
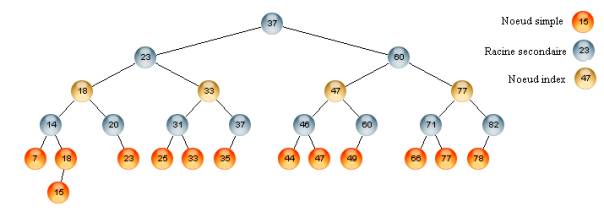
Variant
2 : PBST_rlink
The
PBST_rlink is proposed to improve the operations on the partitions and the
range query operations in the PBST_r.
The
PBST_rlink uses an additional field at the level of node partitions to
stock a pointer to the
partition to the right. This allows to traverse easily all the data
partitions.
The field link is updated only during the merge and split
operations and only on the data partitions
Applications :
Distribution of data on several servers, one partition by server
Parallel treatment on each partition
Images segmentation according to the partitions
Etc.